

So, to retain flexibility, the a #define USE_TIMER at the top of the library header file is used to select which hardware timer is used (1 or 2).Īs TIMER n is a global resource, each object instance of the class must be driven from the same TIMER n interrupt. In the Arduino libraries, TIMER0 is used by the Arduino millis() clock, TIMER1 is commonly used by the Servo library and TIMER2 by the Tone library. The library should work on other Arduino boards (eg, MEGA) with slight modifications, but using it for non-AVR architectures would need extensive rework. It uses either TIMER1 or TIMER2 to implement an interrupt driven clock off which the PWM signal is generated. This library implementation is for AVR processors (specifically Atmel328P processors found on Uno and Nano boards). The limit is a practical solution to the problem of excessive resource being devoted to processing interrupts and is defined as a constant value in the library, easily changed if needed. The MD_PWM library implements user defined frequency PWM output for any digital pin software, limited to 300Hz. However, at low PWM frequencies, this should be a manageable issue.
ARDUINO LED DIMMEN PWM SOFTWARE
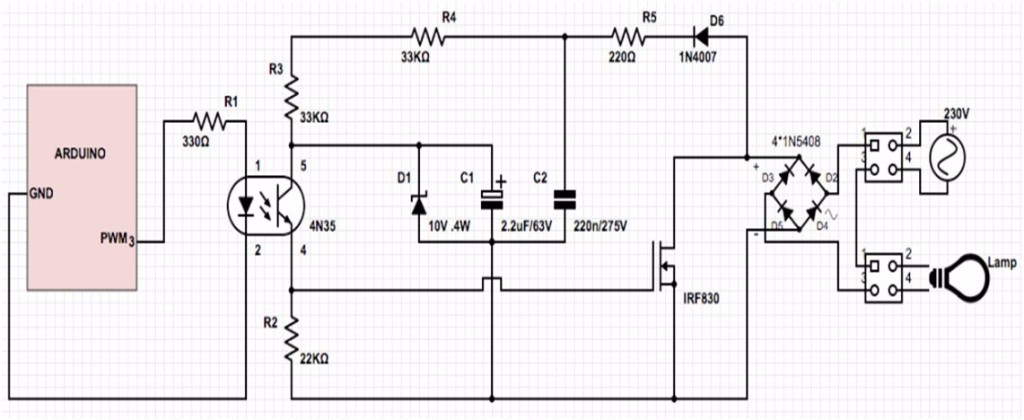
The downside of the software option is that the CPU is used to monitor the time signal and create the PWM digital output, taking processing time away from other tasks. Another is to create a software solution to toggle any output pin at the desired PWM frequency and duty cycle. One solution is to change processor hardware to one with more PWM pins. It would be really useful to have PWM available on more I/O pins. In this case we don’t have enough hardware PWM pins to get the job done (see this previous post about Motor Controllers). Sometimes this is not enough.Īs an example, for two DC motors with a PWM controller, 4 PWM signals are required. So, if an application requires two external interrupts (pins 2 and 3) and an SPI interface (pins 10, 11, 12, 13), there are really only three remaining PWM-capable pins available for additional control. However some of these pins also have very useful alternate functions: Pin The Arduino Uno and Nano use the same processor and have six hardware PWM pins (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11). For 8-bit PWM common on AVR microcontrollers, the duty cycle is controlled by a number between 0 and 255 (0% and 100%). Most microcontrollers have PWM generation hardware built into the processor’s output pins. The longer the signal is ‘on’ compared ‘off’, the higher the total power that can be supplied to the load. A 50% duty cycle is what is commonly called a ‘square’ wave. The duty cycle of a PWM signal is the proportion of ‘on’ time to signal’s total time, given as a percentage. The average voltage and current available to the load are controlled by turning the signal on and off at a fast rate (square wave). Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical digital signal by chopping it up into discrete parts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
